

We will calculate for the entire population. Google Sheets has simple formulas to calculate the standard deviation of a sample or an entire population - STDEV.P or STDEV.S. Step 2: Calculate the standard deviation for the Z-score formula Next, we’ll calculate the standard deviation. Where value1 refers to the data range for which the formula returns a mean. We can obtain the mean value of the dataset using the AVERAGE formula in Google Sheets. Step 1: Calculate the mean for the z-score formula We will analyze this data using the Z-score formula to understand each point’s performance relative to the mean. The image above represents profits a Startup made in the past year.

In the following steps, we will obtain the mean and standard deviation of the data set below. To calculate Z-score in Google Sheets we simply have to obtain all the values needed for the Z-score formula.
#Z SCORE CALCULATOR WITH STANDARD DEVIATION HOW TO#
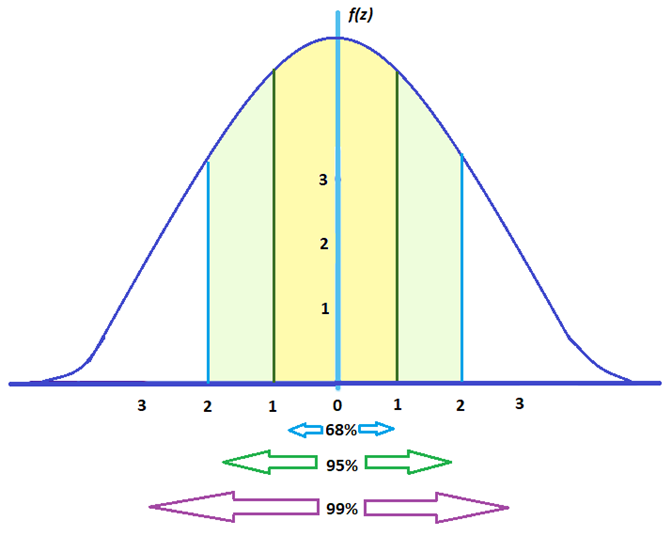
How to calculate Z-score in Google Sheets And it is important for calculations of the normal distribution of samples. This is known as the empirical rule in statistics. Note: In most large datasets, 99% of the data points will be between -3 and 3 standard deviations away from the mean. Therefore, the Z-score is an expression of the standard deviation and tells us how much of its value a point is below or above the mean. Mathematically, it is given as the square root of the variance. The standard deviation considers how spread out each point is from the mean. Stdev (The standard deviation) is a representation of the variability i.e variance of the points in the dataset.It represents the central value that other values in the set tend towards or are spread about. The mean of the distribution is the average value of a given data set.Where the parameters of this function are: Syntaxįormula to calculate z-score in Google Sheets: Z = (Datapoint - Mean)/Stdev But before the examples let’s briefly look at the underlying concepts of the Z-score formula. This tutorial aims to show you how to do this using simple and easy-to-follow examples. We can conveniently calculate the Z-score of a distribution in Google Sheets. Such data points can either be on the negative side of the mean which means below the mean value or on the positive side which means above the mean value. With appropriate historical data, analysts can create samples and distributions through which they examine data points of interest relative to the central value. Knowledge of this relationship can be vital for analysis in areas such as finance where traders can apply it in calculating market volatility and a company can ascertain its closeness to bankruptcy. Given that most points should tend towards a central value, one can make informed decisions based on the behaviour of data points in a sample relative to the mean. Traders and statisticians can determine normal and abnormal values in a given data sample. Introduced by Edward Altman in the 1960s, the Z-formula is widely used widely in the business realm. Which means it is 3 standard deviations from the mean. The Z-score of a distribution or sample is a statistical value that represents how many standard deviations away from the mean a given data point is.įor instance, if a data point is located at point 3 on the X-axis of a normal distribution graph with the mean at zero, that point is said to have a Z-score of 3. We can obtain this Z-score by using the Z-formula in Google Sheets to examine a given data set. It is used to represent the relationship between a value in a data set and the mean. The Z-score is an important tool employed in several analyses. How to calculate z-score in Google Sheets.D3 is the mean of the dataset E3 is the standard deviation. This will return the z-score of the value in cell B3.
Stdev – The standard deviation of the dataset. The Z-score of a distribution is a statistical value that represents how many standard deviations away from the mean a given data point is.įormula to calculate z-score in Google Sheetsĭatapoint – The data for which to calculate the z-score.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
